-
프로그래머스 LV2 - 251023알고리즘 2025. 10. 23. 13:01
LV2. 다음 큰 숫자

class Solution { public int solution(int n) { String binaryVal = Integer.toBinaryString(n); int oneCnt = countOne(binaryVal); int tmpCnt = 0; int answer = n; while (oneCnt != tmpCnt) { answer++; String tmpBinaryVal = Integer.toBinaryString(answer); tmpCnt = countOne(tmpBinaryVal); } return answer; } private int countOne(String binaryVal) { int answer = 0; String[] tmpStr = binaryVal.split(""); for (String x : tmpStr) { if (x.equals("1")) { answer += 1; } } return answer; } }
이번에도 정답은 맞는데 효율성에서 틀렸다
먼저 이진수로 변환한 다음에 1, 0을 사용해서 답을 찾는 로직을 세워봤는데 쉽지 않았다
더 이상 시간 끌 수 없어서 포기하고 정답을 봤다
// 문제가 개편되었습니다. 이로 인해 함수 구성이나 테스트케이스가 변경되어, 과거의 코드는 동작하지 않을 수 있습니다. // 새로운 함수 구성을 적용하려면 [코드 초기화] 버튼을 누르세요. 단, [코드 초기화] 버튼을 누르면 작성 중인 코드는 사라집니다. class TryHelloWorld { public int nextBigNumber(int n) { int postPattern = n & -n, smallPattern = ((n ^ (n + postPattern)) / postPattern) >> 2; return n + postPattern | smallPattern; } public static void main(String[] args) { int n = 78; System.out.println(new TryHelloWorld().nextBigNumber(n)); } }이진수가 나올 때 비트연산자는 고려도 안 했는데... 이렇게 짧은 코드의 답이 나올 수 있었다
비트 연산(bitwise operation)
정수를 2진수로 표현했을 때, 각 비트에 대해 연산을 수행하는 방법
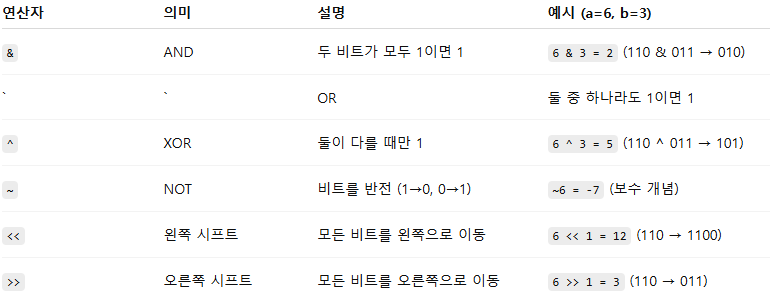
- int postPattern = n & -n; : 가장 낮은 1비트(LS1B)를 뽑아낸다
- n=78 (0b1001110) > postPattern = 0b10 (2)
- -n : 2의 보수 (-n = ~n(n의 비트를 전부 반전)+ 1)
- int smallPattern = ((n ^ (n + postPattern)) / postPattern) >> 2;
- n + postPattern : 뽑아낸 1비트 위치가 캐리를 일으켜 오른쪽 연속된 1 묶음을 깨뜨린다
- 0b1001110 + 0b10 = 0b1010000
- n ^ (n + postPattern) : 변한 비트들만 1로 표시한 마스크를 얻는다
- 0b1001110 ^ 0b1010000 = 0b0011110
- 그 마스크를 postPattern으로 나눠서 정규화하고 >> 2로 두 칸 더 오른쪽으로 밀어
깨진 1들의 개수를 가장 낮은 쪽으로 압축 - 0b0011110 / 0b10 = 0b001111
- 0b001111 >> 2 = 0b000011 → smallPattern = 3
- return n + postPattern | smallPattern;
- n + postPattern으로 01→10을 만들고
- | smallPattern으로 오른쪽에 몰아야 할 1들을 가장 낮은 자리부터 채운다
- 0b1010000 | 0b000011 = 0b1010011 = 83





import java.lang.Integer; class TryHelloWorld { public int nextBigNumber(int n) { int a = Integer.bitCount(n); int compare = n+1; while(true) { if(Integer.bitCount(compare)==a) break; compare++; } return compare; } public static void main(String[] args) { TryHelloWorld test = new TryHelloWorld(); int n = 78; System.out.println(test.nextBigNumber(n)); } }
더 간단하고 이해하기 쉬운 다른 풀이로 bitCount 메서드를 사용하면 가능했다
나는 bitCount 메서드를 몰라서 직접 구현하니까 시간 초과된 거고...
흐음 아쉬워
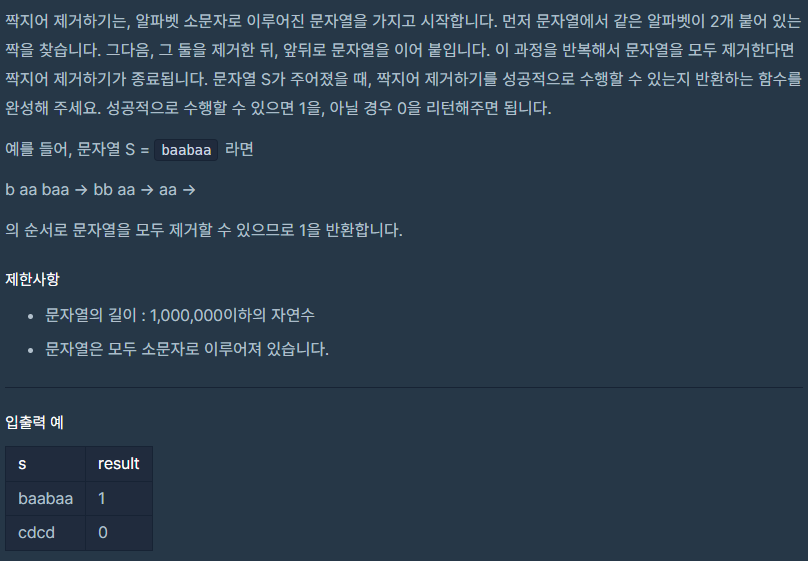
LV2. 짝지어 제거하기
class Solution { public int solution(String s) { int i = 0; int cnt = s.length()/2; String lVal = ""; String rVal = ""; // 홀수 문자열 먼저 제거 if (s.length()%2 != 0) { return 0; } // b aa baa → bb aa → aa → while (cnt >= 0) { lVal = s.substring(i, i+1); rVal = s.substring(i+1, i+2); if (rVal.equals(lVal)) { s = s.substring(0, i) + s.substring(i+2); i = 0; } else { i++; } cnt --; } if (s.isEmpty()) { return 1; } return 0; } }import java.util.*; class Solution { public int solution(String s) { if ((s.length()%2) != 0) { return 0; } String[] tmpStr = s.split(""); Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList<>(); for (String x : tmpStr) { queue.offer(x); } String rVal = ""; String lVal = ""; String tmpVal = ""; int cnt = 0; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { cnt++; lVal = queue.poll(); rVal = queue.peek(); if (!lVal.equals(rVal)) { queue.offer(lVal); } else { queue.poll(); } if (cnt == (s.length()*2)) { return 0; } } return 1; } }큐로 풀어봤는데도 시간 초과 나왔다
> 회전 기반 풀이는 최악에선 O(n²)에 가깝게 늘어날 수 있다
class Solution { public int solution(String s) { if ((s.length()%2) != 0) { return 0; } Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>(); for (char c : s.toCharArray()) { stack.push(c); } String rVal = ""; String lVal = ""; String tmpVal = ""; while (stack.size() > 0) { if (tmpVal.isEmpty()) { rVal = stack.pop().toString(); lVal = stack.pop().toString(); if (!rVal.equals(lVal)) { tmpVal = lVal + rVal; } } else { rVal = stack.pop().toString(); if (tmpVal.substring(0,1).equals(rVal)) { tmpVal = tmpVal.substring(1); } else { tmpVal = tmpVal + rVal; } } } if (tmpVal.isEmpty()) { return 1; } return 0; } }스택으로 풀었을 때 역시 시간초과, 그리고 "abcddcba"와 같은 예시를 실행시켰을 때 stack size가 먼저 0이 되어 틀린 답이 나온다
조금만 더 하면 풀 수 있을 것 같은데 시간 아까우니 정답 보기

class Solution { public int solution(String s) { char[] st = new char[s.length()]; int top = -1; for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) { char c = s.charAt(i); if (top >= 0 && st[top] == c) top--; // 인접 쌍 제거 else st[++top] = c; // 스택에 쌓기 } return top == -1 ? 1 : 0; } }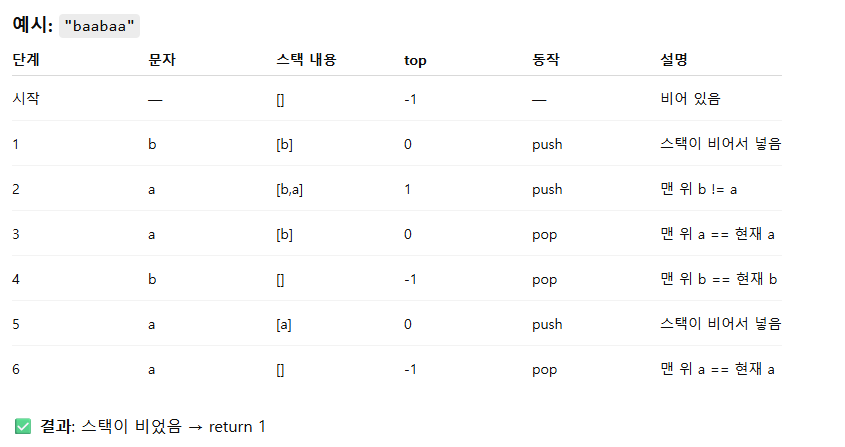
- O(n): 각 문자는 한 번 쌓이고(또는) 한 번 사라짐
- 메모리: char[] n개 → 1,000,000자 기준 약 2MB 수준
- 문자열 가공/박싱 없음 → TLE/메모리 초과 방지
728x90'알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
프로그래머스 LV2 - 251029 (0) 2025.10.29 프로그래머스 LV2 - 251024 (0) 2025.10.24 프로그래머스 LV2 - 251022 (0) 2025.10.22 프로그래머스 LV2 - 251014 (0) 2025.10.14 section7.10 (0) 2025.09.04 - int postPattern = n & -n; : 가장 낮은 1비트(LS1B)를 뽑아낸다