-
리트코드 - 784, 102, 3619알고리즘 2025. 8. 17. 13:02
784. Letter Case Permutation
https://leetcode.com/problems/letter-case-permutation/
Given a string s, you can transform every letter individually to be lowercase or uppercase to create another string.
Return a list of all possible strings we could create. Return the output in any order.
Example 1:
Input: s = "a1b2"
Output: ["a1b2","a1B2","A1b2","A1B2"]
Example 2:
Input: s = "3z4"
Output: ["3z4","3Z4"]
Constraints: 1 <= s.length <= 12
• s consists of lowercase English letters, uppercase English letters, and digits.
public class No1 { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); String str = sc.next(); System.out.println(solution(str)); } public static String[] solution(String str) { Queue<Character> queue = new LinkedList<>(); // str에 몇 개의 문자가 있는지 확인 int charCnt = 1; String tmpStr = ""; for (char x : str.toCharArray()) { queue.offer(x); if (!Character.isDigit(x)) { charCnt = charCnt * 2; tmpStr += x; } } System.out.println("charcnt : " + charCnt); System.out.println("tmpStr : " + tmpStr); // 큐 구조에서 한글자씩 빼서 대문자/소문자 각각 저장, 숫자면 그냥 붙임 // a1b2c // a1 > a1B a1b // A1 > A1B A1b // a1 A1 / a1B a1b A1B A1b / 8 // 2 4 8 16 String[] answer = new String[charCnt]; String[] tmpAnswer = new String[str.length()]; // {{a,A}, {1}, {b, B}, {3}, {C,c} } for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) { char tmpChar = str.charAt(i); for (int y = 0; y < (i+1)*2; y++) { if (i ==0) { String[] tmpArr = new String[(i+1)*2]; tmpArr[y] = String.valueOf(tmpChar).toUpperCase(Locale.ROOT); tmpArr[y] = String.valueOf(tmpChar).toUpperCase(Locale.ROOT); } tmpArr[y] = String.valueOf(tmpChar).toUpperCase(Locale.ROOT); } } return answer; } }- Character.isDigit() 이용해서 숫자인지 문자인지 구분 후 한 글자씩 대소문자로 string을 합쳐가면 될 것 같은데 중복 해결을 어떻게 해야 할지, 배열을 계속 생성해서 다 넣은 다음 최종 결과에서 주어진 string의 길이와 같은 문자열만 return 하면 될까 가 고민이었다
class Solution { public List<String> letterCasePermutation(String s) { List<String> result = new ArrayList<>(); backTracking(result,s.toCharArray(),0); return result; } private void backTracking(List<String> result, char[] chars, int i){ if (i == chars.length){ result.add(new String(chars)); return; } char c = chars[i]; if (Character.isLetter(c)) { backTracking(result,chars,i+1); if (c >= 'a' && c <= 'z'){ chars[i] = Character.toUpperCase(c); backTracking(result,chars,i+1); } else if(c >= 'A' && c <= 'Z'){ chars[i] = Character.toLowerCase(c); backTracking(result,chars,i+1); } } else{ backTracking(result,chars,i+1); } } }- 백트래킹 알고리즘을 활용해서 풀면 되는 문제였다
- 백트래킹 알고리즘을 모르니 풀 수 있을 수가...
- 백트래킹 + DFS 풀이
- BFS 풀이 > 큐에 넣고 큐 사이즈로 이중 for문 돌림, DFS보다 성능이 더 좋을 수 있지만 string > char[] > string 으로 하는 과정에서 속도가 느려짐
102. Binary Tree Level Order Traversal
https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal/description/
Hint
Given the root of a binary tree, return the level order traversal of its nodes' values.
(i.e., from left to right, level by level).
Example 1:
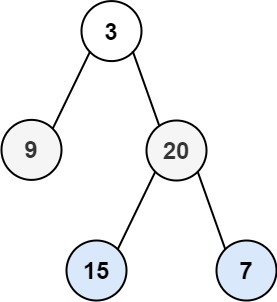
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: [[3],[9,20],[15,7]]
Example 2:
Input: root = [1]
Output: [[1]]
Example 3:
Input: root = []
Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 2000].
- -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
// 1. Recursion(DFS) - 깊이우선탐색 public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>(); levelorderTraversal(result,0,root); return result; } private void levelorderTraversal(List<List<Integer>> result, int level, TreeNode node) { if(node == null){return;} if(result.size() <= level){ // 현재 level List가 없을 경우 ex)size가 1이면 0뎁스까지밖에 없음. 1뎁스일때 만들어줘야함. List<Integer> row = new ArrayList<>(); row.add(node.val); result.add(row); }else{ List<Integer> row = result.get(level); row.add(node.val); } levelorderTraversal(result, level+1,node.left); levelorderTraversal(result, level+1,node.right); }// 2. BFS with Queue - 너비우선 탐색 public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder2(TreeNode root) { List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>(); if (root == null)return result; Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>(); q.offer(root); while(!q.isEmpty()){ int qSize = q.size(); List<Integer> row = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < qSize; i++) { TreeNode cur = q.poll(); row.add(cur.val); if(cur.left != null) q.offer(cur.left); if(cur.right != null) q.offer(cur.right); } result.add(row); } return result; }- BFS > tree 혹은 graph 데이터 구조를 탐색하기 위한 알고리즘
- DFS
- 주어진 tree 혹은 graph의 임의 지점으로 시작해 주위 노드들을 탐색한 후에 다음 층 (level)으로 이동해 탐색을 계속한다
- DFS / BFS 공부하기
- while 문으로 돌리면 size로 안 돌렸을 때 뒤에 남은 것들까지 뽑힐 수 있기 때문에 조심해야함
3619. Count islands with total value divisible by K
You are given an m x n matrix grid and a positive integer k. An island is a group of positive integers (representing land) that are 4-directionally connected (horizontally or vertically).
The total value of an island is the sum of the values of all cells in the island.
Return the number of islands with a total value divisible by k.
Example 1:
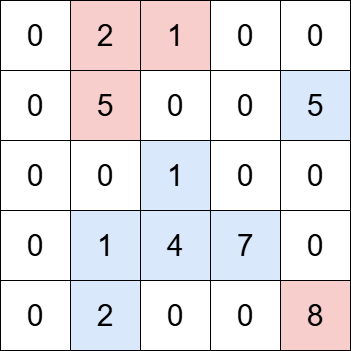
Input: grid = [[0,2,1,0,0],[0,5,0,0,5],[0,0,1,0,0],[0,1,4,7,0],[0,2,0,0,8]], k = 5
Output: 2
Explanation:
The grid contains four islands. The islands highlighted in blue have a total value that is divisible by 5, while the islands highlighted in red do not.
Example 2:
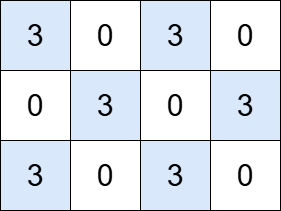
Input: grid = [[3,0,3,0], [0,3,0,3], [3,0,3,0]], k = 3
Output: 6
Explanation:
The grid contains six islands, each with a total value that is divisible by 3.
Constraints:
- m == grid.length
- n == grid[i].length
- 1 <= m, n <= 1000
- 1 <= m * n <= 105
- 0 <= grid[i][j] <= 106
- 1 <= k <= 106
- 방문체크하는 경우 - visited라는 그리드 하나 만들어서 방문 여부 기록하는 그리드 만들거나 차례대로 탐색하면서 0으로 초기화해서 풀 수 있음
- 후자의 경우 공간복잡도?가 줄어들 수 있음 ??, 속도가 빨라짐 ...!
cf. m 문제는 조금 어려울 수 있으니 리트코드 기준으로 아래 유사문제 에서 제일 쉬운 문제 먼저 푸는 것 추천, m 문제도 약간 응용이 들어가 있음
https://ifuwanna.tistory.com/382
728x90'알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
section6.2 (0) 2025.08.20 section6.1 (0) 2025.08.20 section5.8 (1) 2025.08.16 section5.7 (0) 2025.08.15 section5.6 (1) 2025.08.15