-
[스프링MVC - 1편] 스프링 MVC 기본기능 - 1스프링&스프링부트 2025. 1. 28. 17:42
HTTP 요청 - 기본, 헤더 조회
RequestHeaderController
@Slf4j @RestController public class RequestHeaderController { @RequestMapping("/headers") public String headers(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HttpMethod httpMethod, Locale locale, @RequestHeader MultiValueMap<String, String> headerMap, @RequestHeader("host") String host, @CookieValue(value = "myCookie", required = false) String cookie ) { log.info("request={}", request); log.info("response={}", response); log.info("httpMethod={}", httpMethod); log.info("locale={}", locale); log.info("headerMap={}", headerMap); log.info("header host={}", host); log.info("myCookie={}", cookie); return "ok"; } }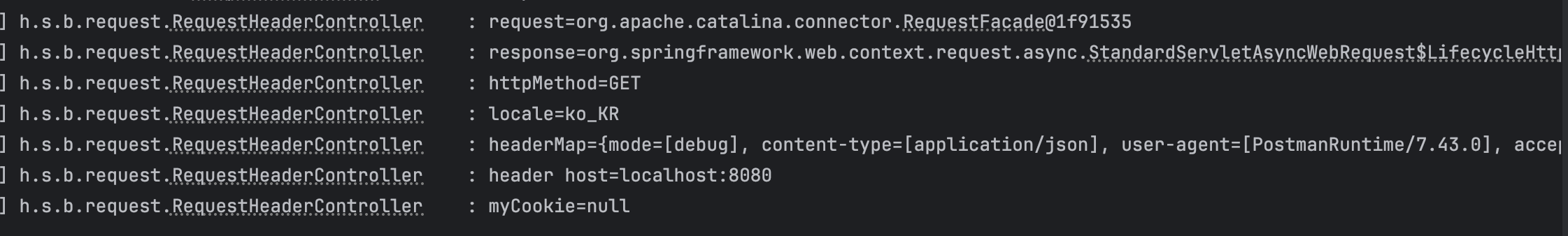
- HttpServletRequest
- HttpServletResponse
- HttpMethod : HTTP 메서드를 조회한다
- Locale : Locale 정보를 조회한다
- @RequestHeader MultiValueMap<string, string=""> headerMap</string,> : 특정 HTTP 헤더를 조회한다
- @RequestHeader("host") String host : 특정 HTTP 헤더를 조회한다
- 속성
- 필수 값 여부 : required
- 기본 값 속성: defaultValue
- 속성
- @CookieValue(value = "myCookie", required = false) String cookie : 특정 쿠키를 조회한다
MultiValueMap - MAP과 유사한데, 하나의 키에 여러 값을 받을 수 있다
HTTP header, HTTP 쿼리 파라미터와 같이 하나의 키에 여러 값을 받을 때 사용한다
MultiValueMap<String, String> map = new LinkedMultiValueMap(); map.add("keyA", "value1"); map.add("keyA", "value2"); //[value1,value2] List<String> values = map.get("keyA");1. HTTP 요청 파라미터 - 쿼리 파라미터, HTML Form
HTTP 요청 데이터 조회 - 개요
클라이언트에서 서버로 요청 데이터를 전달할 때는 주로 다음 3가지 방법을 사용한다
- GET - 쿼리 파라미터
- /url**?username=hello&age=20**
- 메시지 바디 없이, URL의 쿼리 파라미터에 데이터를 포함해서 전달
- 예) 검색, 필터, 페이징등에서 많이 사용하는 방식
- POST - HTML Form
- content-type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
- 메시지 바디에 쿼리 파리미터 형식으로 전달 username=hello&age=20
- 예) 회원 가입, 상품 주문, HTML Form 사용
- HTTP message body에 데이터를 직접 담아서 요청
- HTTP API에서 주로 사용, JSON, XML, TEXT
- 데이터 형식은 주로 JSON 사용
- POST, PUT, PATCH
1. 요청 파라미터 - 쿼리 파라미터, HTML Form
HttpServletRequest의 request.getParameter()를 사용하면 다음 두가지 요청 파라미터를 조회할 수 있다
GET 쿼리 파리미터 전송 방식, POST HTML Form 전송 방식 둘다 형식이 같으므로 구분없이 조회할 수 있다
이것을 간단히 요청 파라미터(request parameter) 조회라 한다
1.1 GET, 쿼리 파라미터 전송
예시 : http://localhost:8080/request-param?username=hello&age=20
1.2 POST, HTML Form 전송
예시 :
POST /request-param ...
content-type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
username=hello&age=20
RequestParamController
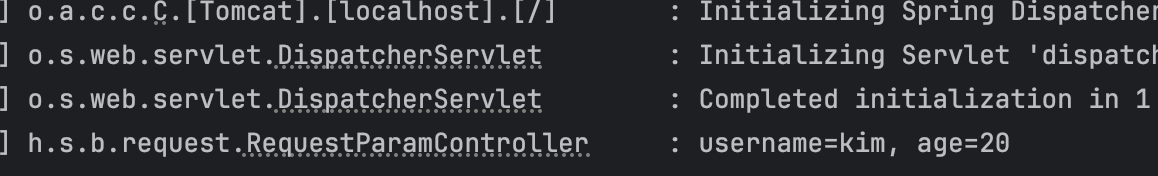
@Slf4j @Controller public class RequestParamController { @RequestMapping("/request-param-v1") public void requestParamV1(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException { String username = request.getParameter("username"); int age = Integer.parseInt(request.getParameter("age")); log.info("username={}, age={}", username, age); response.getWriter().write("ok"); } }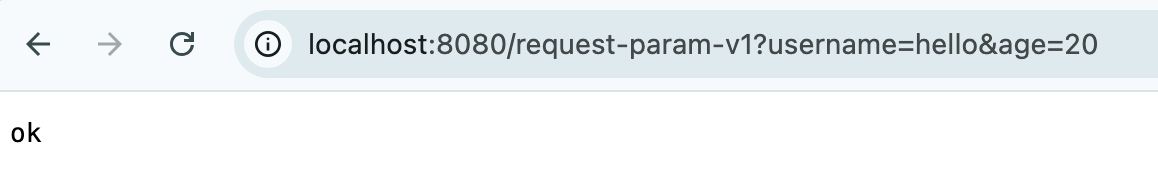
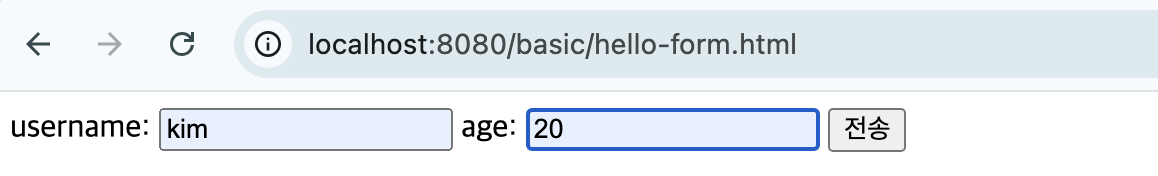
Post Form 페이지 생성
main/resources/static/basic/hello-form.html 생성
2. HTTP 요청 파라미터 - @RequestParam
2-1. requestParamV2
@ResponseBody @RequestMapping("/request-param-v2") public String requestParamV2( @RequestParam("username") String mamberName, @RequestParam("age") int memberAge) { log.info("username={}, age={}", mamberName, memberAge); return "ok"; }- @RequestParam : 파라미터 이름으로 바인딩
- @ResponseBody : View 조회를 무시하고, HTTP message body에 직접 해당 내용 입력
2-2. requestParamV3
@ResponseBody @RequestMapping("/request-param-v3") public String requestParamV3( @RequestParam String username, @RequestParam int age) { log.info("username={}, age={}", username, age); return "ok"; }- HTTP 파라미터 이름이 변수 이름과 같으면 @RequestParam(name="xx") 생략 가능
2-3. requestParamV4
@ResponseBody @RequestMapping("/request-param-v4") public String requestParamV4(String username, int age) { log.info("username={}, age={}", username, age); return "ok"; }- String, int, Integer 등의 단순 타입이면 @RequestParam도 생략 가능
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException
requestParamV3와 requestParamV4의 경우 에러가 발생한다
스프링 부트 3.2부터 자바 컴파일러에 -parameters 옵션을 넣어주어야 애노테이션에 적는 이름을 생략할 수 있기 때문이다
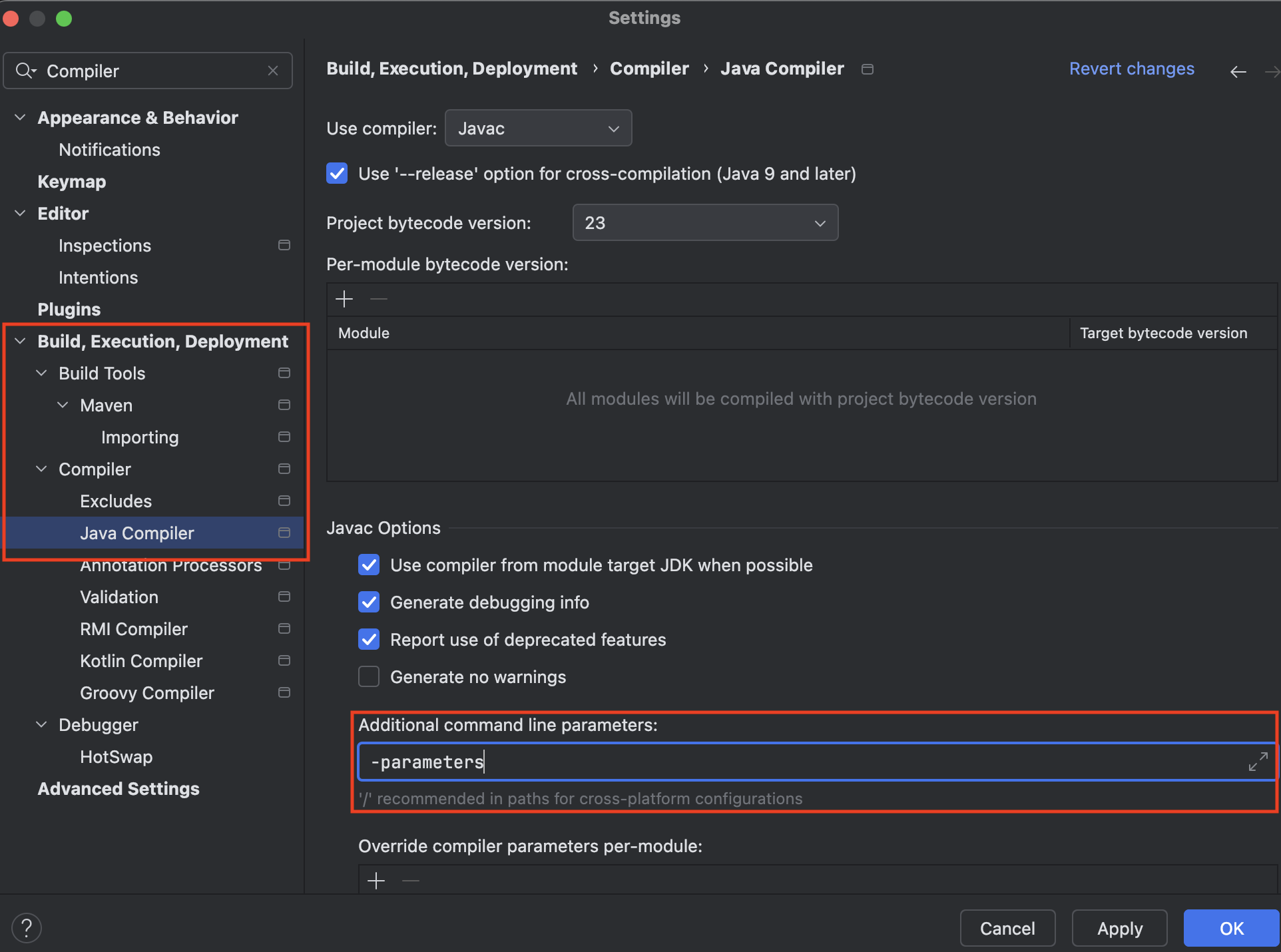
컴파일 시점에 -parameters 옵션 적용하면 해결할 수 있다
IntelliJ IDEA > Settings (command+,) > Build, Execution, Deployment > Compiler > Java Compiler
Additional command line parameters라는 항목에 -parameters 을 추가한다
out 폴더를 삭제하고 다시 실행한다
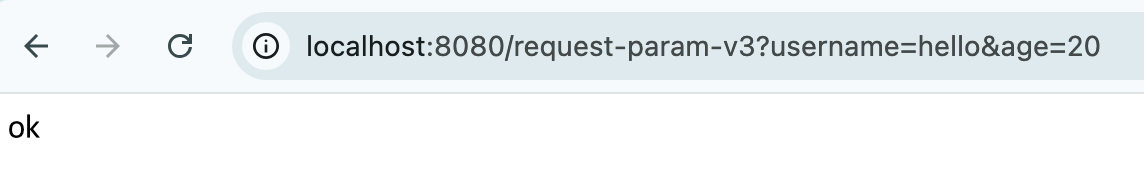
정상 작동함을 확인할 수 있다
2-4. requestParamRequired - 파라미터 필수 여부
@ResponseBody @RequestMapping("/request-param-required") public String requestParamRequired( @RequestParam(required = true) String username, @RequestParam(required = false) int age) { log.info("username={}, age={}", username, age); return "ok"; }- @RequestParam.required : 파라미터 필수 여부, 기본값은 true
- /request-param-required?username= : 파라미터 이름만 있고 값이 없는 경우 빈문자로 통과
- @RequestParam(required = false) int age + /request-param 요청 : null을 int에 입력하는 것은 불가능(500 예외 발생)
- null을 받을 수 있는 Integer로 변경하거나 defaultValue 사용
2-5. requestParamDefault- 기본 값 적용
@ResponseBody @RequestMapping("/request-param-default") public String requestParamDefault( @RequestParam(required = true, defaultValue = "guest") String username, @RequestParam(required = false, defaultValue = "-1") int age) { log.info("username={}, age={}", username, age); return "ok"; }- 파라미터에 값이 없는 경우 defaultValue를 사용하면 기본 값을 적용할 수 있다
2-6. requestParamMap - 파라미터를 Map으로 조회하기
@ResponseBody @RequestMapping("/request-param-map") public String requestParamMap(@RequestParam Map<String, Object> paramMap) { log.info("username={}, age={}", paramMap.get("username"), paramMap.get("age")); return "ok"; }- 파라미터를 Map, MultiValueMap으로 조회할 수 있다
3. HTTP 요청 파라미터 - @ModelAttribute
HelloData
@Data public class HelloData { private String username; private int age; }3-1. modelAttributeV1 - @ModelAttribute 적용
// @ResponseBody // @RequestMapping("/model-attribute-v1") // public String modelAttributeV1(@RequestParam String username, @RequestParam int age) { // HelloData helloData = new HelloData(); // helloData.setUsername(username); // helloData.setAge(age); // return "ok"; // } // @ModelAttribute 사용 @ResponseBody @RequestMapping("/model-attribute-v1") public String modelAttributeV1(@ModelAttribute HelloData helloData) { log.info("username={}, ag={}", helloData.getUsername(), helloData.getAge()); return "ok"; }스프링MVC는 @ModelAttribute가 있으면 다음을 실행한다
- HelloData 객체를 생성한다
- 요청 파라미터의 이름으로 객체의 프로퍼티를 찾는다
- 해당 프로퍼티의 setter를 호출해서 파라미터의 값을 바인딩한다
3-2. modelAttributeV2 - @ModelAttribute 생략
@ResponseBody @RequestMapping("/model-attribute-v2") public String modelAttributeV2(HelloData helloData) { log.info("username={}, age={}", helloData.getUsername(), helloData.getAge()); return "ok"; }- @ModelAttribute는 생략할 수 있다
728x90'스프링&스프링부트' 카테고리의 다른 글
[스프링MVC - 1편] 스프링 MVC 기본기능 - 4 (1) 2025.01.29 [스프링MVC - 1편] 스프링 MVC 기본기능 - 3 (0) 2025.01.29 [스프링MVC - 1편] 스프링 MVC 기본기능 - 요청 매핑 (0) 2025.01.28 [스프링MVC - 1편] 스프링 MVC 기본기능 - 프로젝트 생성 및 로그 (0) 2025.01.28 [스프링MVC - 1편] 스프링 MVC 시작 (0) 2025.01.27